|
DOI: 10.7256/2454-0676.2022.3.36149
EDN: LZWTJI
Received:
23-07-2021
Published:
07-10-2022
Abstract:
The subject of the study is the description and analysis of the solution of practice-oriented tasks in the bachelor's degree in a rapidly changing market of professions (using the example of the web resource of the HSE School of Design). Methodology. Using the example of the HSE School of Design, a competence-based approach to the implementation of practice-oriented education in the design field is described and analyzed. The following research methods were used to solve the tasks and verify the hypothesis put forward: theoretical analysis of philosophical, psychological, pedagogical, special, reference literature on the research problem and generalization of scientific ideas and views; survey (interviewing); conversation, direct and indirect observation. Scientific novelty. The basis of the educational model of teaching designers at the HSE School of Design is the web resource of the HSE School of Design, which combines the "Map of Creative Competencies", "Student Portfolio" and "Design Laboratory". The HSE considers the Design Laboratory as a creative platform for conducting students' industrial practice and a platform for solving practice-oriented tasks of the digital society. Practical significance. A brief analysis of the basics of two educational models is given: the Bauhaus (Germany, Weimar, 1923) and the HSE School of Design (Russia, Moscow, 2021). Results. The parallels of the application of the practice-oriented Bauhaus approach in the teaching of the HSE School of Design of bachelor designers for the digital society are drawn.
Keywords:
higher education, professional competencies, professional development, new educational strategies, formation, general professional competence, bauhaus, map of creative competencies, creative design, level
This article is automatically translated.
You can find original text of the article here.
Introduction The relevance of the article is due to the need to describe the features of modern approaches to training designers for a digital society (using the example of the HSE School of Design) and the features of the formation of a "Map of creative competencies" in the rapidly changing "market of professions" [1]. The purpose of the research is to describe the elements of the formation of creative competencies when creating an educational model of training designers from the point of view of the change of generations X-Y-Z to specialists who have mastered digital competencies, ready to be competitive in a rapidly changing market of professions. The subject of this study is the description of the solution of the contradiction between the educational standard of the Federal State Educational Standard and the professional standard (using the example of the HSE School of Design). The three cornerstones-activators of innovations in the educational process in relation to the content of professional competence (OPC and PC OOP) of undergraduate graduates and the formation of the content of the training direction 54.03.01 "Design" for the digital society are: · state monitoring of the quality of educational services (compliance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, taking into account the geopolitical development of Russia); · on the part of the customer, the requests of the target audience: students (their parents as customers of educational services) for compliance of undergraduate graduates with the requirements of the employer - employability (author of the term Pavel Olegovich Luksha, research scientist, Skolkovo)); · on the part of the employer, the actual content of the subject area of the direction 54.03.01 "Design" in the field of interdisciplinary multitasking of an employee of a digital society. Within the framework of this study, it is not possible to fully describe the course of the study without delving into the psychological and pedagogical aspects of the relationship between the concepts of "creative competencies" and the concepts of "creative abilities", "creative activity" (some aspects were investigated by the author in his PhD thesis). Let's list the step-by-step analysis of the "Map of Creative Competencies" for teaching students of creative profiles of the HSE School of Design:· the objectives of building a "Map of creative competencies" are defined; · a comparative analysis of the requirements of the FGOS generation 3+ (2016) and the draft of the basic requirements of employers 3++ (2017) was carried out; · the reference points for multi-factor criteria (focus on the credit-modular system and point-rating construction of the educational process) are described. The methodological basis of the research conducted by the author used systematic, personal-activity and competence-oriented approaches. The personality-activity approach (L.S. Vygotsky, P.Ya. Galperin, V.V. Davydov, E.F. Zeer, A.N. Leontiev, A.K. Markova, S.L. Rubinstein, etc.) characterizes a personality as a subject of activity within which it is formed, interacts with other personalities, independently determines the nature of actions and communication. The significance of the systematic approach for our research (V.G. Afanasyev, V.P. Bespalko, Yu.K. Babansky, I.V. Blauberg, V.N. Sadovsky, E.G. Yudin, etc.) is that it allows us to consider the formation of students' professional creative potential as a pedagogical system with its inherent properties, features and patterns. In the "Great Encyclopedic Dictionary", the system approach is interpreted as a methodological principle of scientific cognition, consisting in considering objects as systems of various types of connections existing in them. In our study, the main support was on the following interpretation of two terminological definitions from the dictionary edited by S.Y. Batyshev "Encyclopedia of Vocational Education": "... Creativity (from the English creativity) – the ability to productive activity; the personal quality of an individual, expressed in his predisposition and willingness to create, i.e. to make real, socially significant products of his activity.
This means that an individual has a stable motivation to achieve high positive results, as well as the necessary knowledge, understanding of the essence of the matter, skills and abilities. Creativity manifests itself in various forms, the totality of which can be subdivided depending on the orientation, content and level of complexity of creative activity. In all cases, the necessary prerequisite for the success of creative actions is the individual's ability to work, determined by three main factors: a) the state of physical and mental health; b) the general background of life activity that determines social well-being; c) the level of competence, skill, professionalism combined with independence, criticality and constructive thinking." "... Professional competence is an acquired quality of personality, which is determined by the level of formation of professional competencies in a student, which further ensures that a graduate of a higher educational institution is in demand on the labor market, social adaptation in society, self-realization, self-sufficiency." [2] Here is the formulation of the concept of "professional competence" by E. F. Zeer in the 2005 edition "Psychology of Professions": "... Professional competence is an integrative quality of a person's personality, including a system of necessary knowledge, skills and abilities sufficient to perform a certain type of professional activity."The study uses a systematic approach to the analysis of the elements of the educational process of the HSE School of Design as a result of a specific symbiosis of creative activity and business activity (within the framework of project activities in the HSE Design Laboratory). A number of researchers Vodiakha S.A., Gnatyshina E.A., Gerdt N.A. and others. in their research, they describe the process of students obtaining professional knowledge and professional competencies in higher education and the author's assessments of the levels of formation in terms of compliance with the labor market [3, 4]. A competence-oriented approach to the formation of an educational model of training designers for a digital society is logical, since modern Russian education correlates its development in accordance with the requirements of the Bologna Convention. The Russian Federation uses the most widespread ECTS system in Europe (European Credit Transfer System, European Credit Transfer System). The HSE has formed a training system during the academic year for 4 modules with intermediate certification after each module. Credit unit (or Credit) is a universal unit of measurement of the volume of an educational program. At the HSE, one credit unit is equal to 38 academic hours, the duration of one academic hour at the HSE is 40 minutes, one credit unit is slightly more than a full day. Let us explain the main provisions of the analysis of the formation of elements of the educational program of the HSE School of Design. All the materials given are taken from publicly available sources. Wide coverage of creative directions within the framework of the "Design" direction [5] At the HSE School of Design, in the conditions of effective management, training is currently being carried out in several dozen popular areas of training "Design" (bachelor's and master's degrees, additional education, pre-university training, electives): Bachelor's degree (fig. 1) 1. Communication designFont, typography, multi-page edition Branding Motion design 2. Animation and illustrationAnimation
Illustration Multimedia design 3. Visual effects4. Environment design 5. Interior design 6. Design and programming Digital product design and development Mobile development 7. Web design and digital product promotion8. Design and contemporary art 9. Game design and virtual reality 10. Theater and cinema artist 11. Media and Design 12. Design and advertising 13. Comic book 14. Industrial design 15. Fashion / Fashion Design Branding in the fashion industry Fashion photography 16. Photography in fashion and advertising17. Jewelry art and object design in fashion 18. Artist and curator 19. Media art 20. Cinema and video art 21. Sound art and design 22. Modern photography Design (St. Petersburg) Communication design (St. Petersburg) Environment Design (Saint Petersburg) Design (Perm) Communication and digital design (Perm)
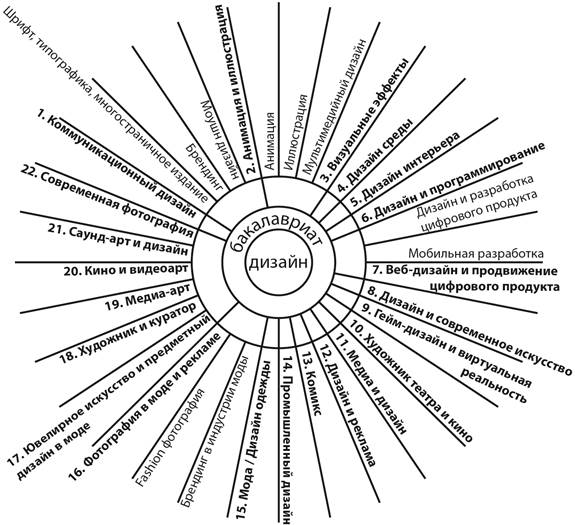
Figure 1. Diagram of areas of training (bachelor, School of Design higher school of Economics, 2019) Fig. 1. Scheme of training areas (Bachelor's Degree, HSE Art and Design School) Master's degree (Fig. 2) Communication and digital design Communication design. Basic level The design and promotion of a digital product Design Art direction City branding and urban design Book art Illustration and graphics Systemic game design Industrial design Interior design Fashion Create a fashion brand Art direction in fashion Practice of modern art Multimedia and digital arts Modern painting Auteur cinema Copyright and commercial animation Modern design in teaching 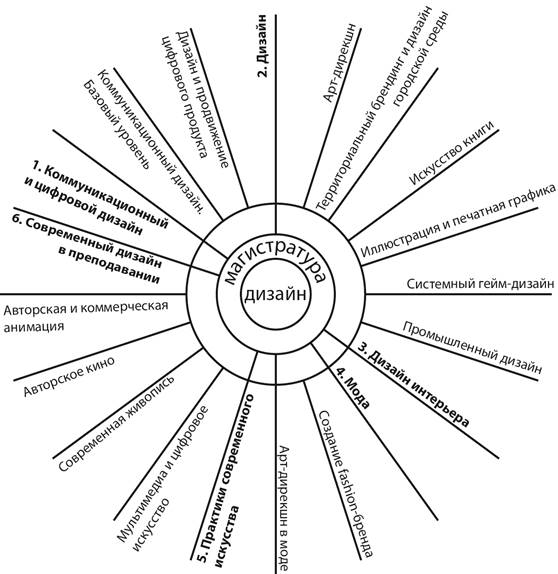
Figure 2. Diagram of areas of training (master's degree, School of Design higher school of Economics, 2019) Fig. 2. Scheme of training areas (Master's degree, HSE Art and Design School) Map (matrix) creative competencies School of design HSE formed taking into account the breadth of profile design activities for the development of creative activity of students. Table 1 the curriculum areas of training 54.03.01. Design (HSE faculty of communications, media and design, Moscow) 2019/2020 academic year Duration of training: 4 years
Years of study: 2019/2020 academic year - 2022/2023 academic year Form of study: full-time Number of students: 489 Education level: Bachelor | Block code, item no. | Name of the discipline | Implementing division | Credits | Total hours | including contact hours | Distribution of contact hours by modules | Add. info. | | | | | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | | | | The entire educational program | 60 |
2480 | 799 | 182 | 164 | 234 | 219 | | | | 1 | Block 1. Disciplines (modules) | 60 | 2480 | 799 | 182 | 164 | 234 | 219 |
| | | B.O | General cycle | 13 | 694 | 236 | 70 | 52 | 58 | 56 | | | | | Block "Life safety" | 1 | 38 | 18 |
18 | | | | | | | 1 | Life safety | student initiative support center | 1 | 38 | 18 | 18A | | | | online disc. | | | 2 | Life safety (taught in English) |
student initiative support center | 1 | 38 | 18 | 18A | | | | online disc., in English. yaz. | | | | The "Sociology" block | 4 | 152 | 32 | 16 | 16 |
| | | | | 3 | Sociology | Department of Sociology | 4 | 152 | 32 | 16 | 16A | | | online disc. | | | 4 | Sociology (taught in English) | Department of Sociology |
4 | 152 | 32 | 16 | 16A | | | online disc.,in English. yaz. | | | | The "Physical Culture" block | | 200 | 144 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
36 | | | | 5 | Physical Culture | Department of Physical Education | 0 | 200 | 144 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36A | | | | 6 | Physical Culture | Department of Physical Education | 0 |
200 | 144 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36A | | | | | The Philosophy Block | 4 | 152 | 40 | | | 20 | 20 |
| | | 7 | Philosophy | School of Philosophy | 4 | 152 | 40 | | | 20 | 20A | online disc. | | | 8 | Philosophy (taught in English.language) | School of Philosophy | 4 | 152 | 40 |
| | 20 | 20A | online disc.., in English. yaz. Digital Literacy Block | | | | | 4 | 152 | 2 | | | 2 | | | | | 9 |
Digital literacy | Design School | 4 | 152 | 2 | | | 2 | a | online disc. | | | 10 | Digital literacy (taught in English) | Design School | 4 | 152 | 2 | |
| 2 | a | online disc., in English. yaz.B.Pr | | | | Professional Cycle (Major) | 47 | 1786 | 563 | 112 | 112 | 176 | 163 | | | | B.Pr.B | The basic part |
47 | 1786 | 563 | 112 | 112 | 176 | 163 | | | | 11 | Internal English Language Exam (1st year) | Department of Foreign Languages | | 6 | 3 | | |
| 3A | | | | | Block "Creative design" | 20 | 760 | 280 | 56 | 56 | 88 | 80 | | | | 12 | Creative design (taught in English) | Design School |
20 | 760 | 280 | 56A | 56A | 88A | 80A | in English. yaz.13 | | | | Creative design | Design School | 20 | 760 | 280 | 56A | 56A | 88A |
80A | | | | | The "History" block | 5 | 190 | 56 | 28 | 28 | | | | | | 14 | History | Design School | 5 | 190 |
56 | 28 | 28A | | | online disc. | | | 15 | History (taught in English) | Design School | 5 | 190 | 56 | 28 | 28A | | | online disc., in English. language | |
| | Block "History and theory of design" | 10 | 380 | 84 | | | 44 | 40 | | | | 16 | History and theory of design | Design School | 10 | 380 | 84 | |
| 44 | 40A | online discipline. | | | 17 | History and Theory of design (taught in English) | Design School | 10 | 380 | 84 | | | 44 | 40A | online disc., in English. yaz.Art Practice Block | | | | |
12 | 456 | 140 | 28 | 28 | 44 | 40 | | | | 18 | Art practice | Design School | 12 | 456 | 140 | 28A | 28A |
44A | 40A | | | | 19 | Art practice (taught in English) | Design School | 12 | 456 | 140 | 28A | 28A | 44A | 40A | in English. yaz. | | | B.F | Electives | 0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | | | 20 | English language * | Department of Foreign Languages | 8 | 304 | 144 | 32 | 32A | 40 |
40 | does not teach. in the current. rei tingNumber of weeks: | | | | | | | 35 | | 7 | 7 | 11 | 10 | | | Note. A Interim certification * Credits are counted only in the cumulative rating [5, Ibid.] Table 2 Functional model of the relationship of the Map of creative competencies (including interaction with the Creative portfolio of students)Functional components | Actual content | informative | |
|
Summary of the training material | | activityTasks, examples of work | | | interactiveOnline assessment tools, web forums for viewing the project on external Vimeo resources (and similar), publishing the project in social networks Facebook, VK (Vkontakte), Twitter | | | methodicalRecommendations on the use of the resource in training, (including point-rating and credit-modular assessment components) | | | organizationalContact information, class schedule | | The object-object interaction is briefly described in tabular form with a brief analysis of the functional content of the "Map of Creative Competencies" in relation to the "Creative Portfolio of students". The main division of the professional educational program "Design" takes place in 4 main blocks: "Project", "Technology", "Art practice/Writing", "History and theory" (see Fig.3). 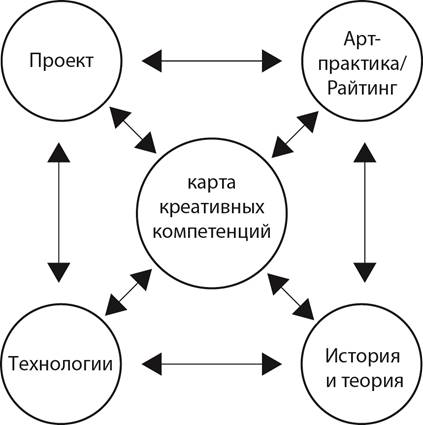
Figure 3. Components of the creative competence map of the HSE School of Design for solving practice-oriented tasks Fig. 3. Components of the creative competence map of HSE Design School for practice-oriented tasks Depending on the chosen direction of training, students master different elements of the OOP, but the above 4 blocks remain the main ones. Let us explain that the main provisions of the conducted research were carried out regarding the analysis of the direction of training "Communication design" (profile "Font, typography, multi-page edition"). "Creative design". A system-forming discipline is a "Project", within the framework of which the basics of corporate identity, visual identification systems, multi-page publications and other forms of multimedia product design are created during the academic year for one brand (fantastic, fictional or real).
Students learn to think systematically by stringing various technologies of the project concept onto one visual idea to present to the customer (from the presentation of graphic constants to the visualization of 3-dimensional three-dimensional compositions of the interior, a brochure or a staged and mounted video). Training sessions are held in classrooms equipped with computers with licensed software installed (editors for creating and processing graphics, sounds and animation). "Technologies". Students of all areas of training "Design" in the first year of study master the technologies of working with vector, raster (pixel) graphics, layout and animation in modern graphic editors (licensed package Adobe Creative Clouds) in one volume or another, depending on the chosen profile of the main educational program of the PLO. This package of graphic editors is currently basic for all designers and is a mandatory item in all requests of design workers by recruiting organizations. "Art practice/Writing". The main propaedeutic tasks of developing creative activity are solved during the first year of study by students of all training profiles in the process of studying such academic disciplines as "Art Practice", "Sketching", "Illustration", "Art Project" (within which collective work on one project is organized with the distribution of roles as in design and advertising bureau). At the HSE School of Design, academic drawing and painting are not taught in full in the classical form of teaching these disciplines (sitters, still life productions, etc.). In the course of training, senior students master "History and theory". The block of historical disciplines covers the study of large periods of art, styles and trends from the history of visual communications, industrial design, graphic design, architecture and interior, Art direction and production, photography, cinema, theater, fashion, animation, books, etc. to the smaller in volume, but not in importance, history of the Russian avant-garde, the history of material culture, the history of comics, video games, media culture, scenography, costume, the basics of drama, etc. The duration of courses varies from 1 credit to 8 (in English). The study briefly describes the content and functional features, formulated criteria for evaluating the Creative Competence Map and Student Portfolio, designed to improve the educational process in the Design Bachelor's degree. The author analyzes the use of distance learning on the Open Education platform and Coursera. Free online courses "Introduction to the History of Art", "History of Design" (authors A.K. Dezhurko, A.D. Staruseva-Persheeva), "History of Advertising Tools" (author A.N. Alekseev), "Modern Art" (author A.O. Zhuravlev) have been created on this platform by teachers of the HSE School of Design and others . Taking English-language Coursera courses is included in the mandatory curriculum of senior students of the HSE School of Design. Online courses of the block "History and Theory" are studied at the senior courses of the PLO by choice in English on the Coursera platform [6]. In addition to compulsory disciplines, students can choose variable disciplines from another training profile, thereby enriching their individual training plan with knowledge from the history of another professional field of design and advertising.Here is an example of a list of variable disciplines of the block "History and theory of design" (module 1) History of Cinema (Part 1) 1 credit Popular Culture (Part 1) 1 credit Animation History (Part 1) 1 credit History of Photography (Part 1) 1 credit The History of Media Culture (Part 1) 1 credit Special and Visual Effects: History and Technology (Part 1) 1 credit Video Game History (Part 1) 1 credit Advertising History (Part 1) 1 credit History of the book (Part 1) 1 credit Architectural monuments of the Moscow region (part 1) 1 credit Comic Book History (Part 1)
We will reveal in more detail the content of some academic disciplines. "History of Art" (1, 2 parts). The study of the evolution of the development of fine art, sculpture, architecture enriches students with knowledge of the theory of the formation and development of types, genres, styles of art. In the classroom, students learn to analyze, attribute, and isolate stylistic features of works of art. The skills of describing and analyzing artifacts mastered by students help in further training when creating visual studies, which form the basis of work on the final qualifying work (WRC). "The history of design" is a mandatory element of the educational program, studied in the format of an online course. "Modern Art" (1, 2 parts). The study of all periods of the development of modern art of the twentieth century through the prism of the causes, stylistic features, discussion of the creativity of the most prominent representatives from the first avant-garde trends (Fauvism, expressionism, Cubism, Russian avant-garde, futurism, Dadaism, new materiality, abstract expressionism, pop art, Tashism, new realism, kineticism, minimalism, conceptualism and etc.) until today. "The history of advertising" (1, 2 parts). This segment of the educational program is studied by all students (depending on the direction in different courses) online. "The History of industrial design" (1, 2, 3 parts). The training course includes a brief chronological overview of the national design schools of Europe and America (England, Germany, the Netherlands, France, Italy, etc. states) and major designers, leading schools, museums and exhibition spaces. Results and discussion.Let's summarize the intermediate stage of the study of the principles of forming a map of creative competencies of the HSE School of Design from the point of view of comparative analysis: a curious analogy with the Bauhaus school is being built. Here is a parallel analysis of the basics of two educational models: the Bauhaus and the HSE School of Design. 1 year of study at the HSE is similar to the Vorlehre (German), pre-apprenticeship (English), introductory course (Russian), pre-training of the Bauhaus Design School (Bauhaus, Hochschule f?r Bau und Gestaltung — Higher School of Construction and Artistic Design, or Staatliches Bauhaus, Weimar Germany), which existed for 14 years from 1919 to 1933 (see Fig. 4) [5]. 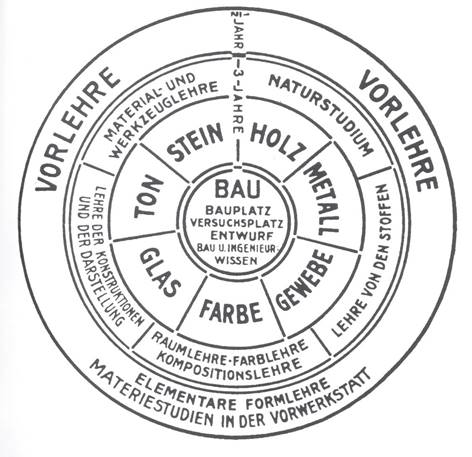
Figure 4. The scheme of training in the Bauhaus. (Germany, Weimar, 1923) [7] Fig. 4. Scheme of training in the Bauhaus. (Germany, Weimar, 1923) The course of the Bauhaus design school initially introduced students of post-reform Germany to various materials and technologies for processing fabric, wood, paper, glass, metal, etc. materials and technologies. Thus, in the Bauhaus School of Design, already in the first year, the tasks of practice-oriented training of designers for the needs of textile, printing, construction, furniture, glass and other various industries were solved. At the senior courses, future designers of the 20s in Germany, as artisans, had to sculpt (draw, print, chisel, sculpt, saw, weave) objects of industrial, environmental and graphic design with their own hands on machine tools and specialized equipment. Students of the HSE School of Design are introduced in practice to the basics of creative design design in Adobe Master Collection graphic editors by modules (HSE has adopted a graduation by modules, similar to the quarters of the school academic year). This time (modular) principle correlates with the credit-modular system and the point-rating evaluation of the results of creative activity. The choice of Adobe Master Collection is absolutely logical, because it includes the main graphic editors as tools of the designer of the digital society. In module 1, "Fundamentals of Design", students master the Adobe Illustrator graphic editor as a technology at a basic level. Next, in the 2nd module "Fundamentals of Visual Communication" comes the stage of mastering the Timble Navigation SketchUp environmental design editor and Adobe Photoshop raster (pixel) graphics. Students in module 3 "Fundamentals of Multi-page publication Design" are mastered in the Adobe InDesign layout and layout editor. And finally, in module 4 of the 1st course of study "Fundamentals of Corporate Identity Creation", students master the basics of motion design Adobe After Effects and Adobe Premier in graphic editors.
First-year undergraduate students master the basic skills of creating a corporate identity with the task of developing a corporate identity of a fictional, fantastic project and writing an essay about it, combining them into a common system subordinated to a single logic and plastic, so that each of the elements of this system corresponds to a common project concept. Familiarization with all the basic standards for processing graphics, sound, animation, visualization of graphic ideas on media (business cards, letterheads, souvenirs) takes place during the training process under the supervision of a curator, the results of the design by students are independently uploaded to the Student Portfolio website. Excellent practice to keep up with the deadline (English limit, limit) as a strict time limit on the execution time, it teaches students to be careful in the use of time for design. There are the most important advantages of learning in the creative field, this is the introduction of intellectual property products (read, own creative developments in design), which ensure the rapid transition of research results to the stage of practical application. This is the way to create developments for the implementation of the Strategy of Scientific and Technological Development of the Russian Federation for the long term [8]. Professional evaluation of projects takes place during the session by the examination commission (which includes employers as representatives of the business sphere) and informal evaluation by all visitors of the web resource. The point-rating evaluation of the results of students' creative activity is correlated by the acquired competencies using their own evaluation system [9]. HSE has adopted its own system for assessing acquired competencies: in the description of HSE educational standards, the formulations of specific competence-based educational results from among professional ones differ (in order to more accurately reflect professional or subject specifics, ensure accessibility and transparency of formulations for the main target groups), but they are classified and codified in accordance with the proposed competencies (Table.3 FGOS IN 2016). Let's compare the lists of professional competencies that differ by 1 year 2016 and 2017. We conclude that, in general, a fairly detailed list of descriptions of professional competencies in the 2016 project succinctly and very briefly conveys the framework of the 2017 competence project (introduced in January 2020), which will be filled with content by the developers of the OPOP in each university. The developers of the OPOP of all design universities will make adjustments until January 2020 in terms of filling each academic discipline of the curriculum. But the emphasis is already visible in the interpretation of this list of competencies through the ability (see Table 3) as a category of personality for mastering the profession of a graphic designer of visual information, identification and communication (see Table 4). Table 3 "…List of competencies comparative analysis of the requirements of the 3rd+ generation Federal State Educational Standard (direction 54.03.01 "Design") (2016) and the requirements of potential employersCode | Name of the learning result | general cultural competencies: | | | OK-1 | | the ability to use the fundamentals of philosophical knowledge to form a worldview position | |
| OK-2the ability to analyze the main stages and patterns of the historical development of society for the formation of a civic position | | | OK-3ability to use the basics of economic knowledge in various fields of activity | | | OK-4ability to use the basics of legal knowledge in various fields of activity | | | OK-5ability to communicate orally and in writing in Russian and foreign languages to solve problems of interpersonal and intercultural interaction; | | | OK-6ability to work in a team, tolerantly perceiving social, ethnic, confessional and cultural differences | | | OK-7ability to self-organize and self-education | | | OK-8the ability to use methods and means of physical culture to ensure full-fledged social and professional activities | | | OK-9 |
ability to use first aid techniques, methods of protection in emergency situations | | OK-10ability to abstract thinking, analysis, synthesis | | | OK-11willingness to act in non-standard situations, to bear social and ethical responsibility for the decisions taken | | | | about professional competencies:OPK-1 | | the ability to own a drawing, the ability to use drawings in the practice of composing and processing them in the direction of designing any object, to have the skills of linear-constructive construction and to understand the principles of choosing the technique of execution of a particular drawing | | | OPK-2knowledge of the basics of academic painting, techniques of working with color and color compositions | | | OPK-3ability to possess the initial professional skills of a sculptor, techniques of work in layout and modeling | | | OPK-4 |
the ability to apply modern font culture and computer technologies used in design design | | OPK-5ability to implement pedagogical skills in teaching art and design disciplines (modules) | | | OPK-6ability to solve standard tasks of professional activity on the basis of information and bibliographic culture with the use of information and communication technologies and taking into account the basic requirements of information security | | | OPK-7the ability to search, store, process and analyze information from various sources and databases, present it in the required format using information, computer and network technologies | | | professional competencies corresponding to the type (types) of professional activity that the bachelor's degree program is focused onartistic activity: | | | PC-1 | | the ability to master the drawing and techniques of work, with the justification of the artistic idea of the design project, in layout and modeling, with color and color compositions | | | PC-2the ability to substantiate their proposals when developing a project idea based on a conceptual, creative approach to solving a design problem | | | PC-3 |
the ability to take into account the features of materials in the development of an artistic idea, taking into account their formative properties; | | | project activities:PC-4 | | the ability to analyze and determine the requirements for a design project and synthesize a set of possible solutions to a problem or approaches to the implementation of a design project | | | PC-5the ability to design objects, goods, industrial designs, collections, complexes, structures, objects, including to create an accessible environment | | | PC-6the ability to apply modern technologies required in the implementation of a design project in practice | | | PC-7the ability to perform reference samples of a design object or its individual elements in a layout, material | | | PC-8ability to develop a product design taking into account manufacturing technologies: to carry out technical drawings, to develop a technological map of the execution of a design project | | | |
information technology activities:PC-9 | | the ability to make a detailed specification of requirements for a design project and prepare a complete set of documentation for a design project, with basic economic calculations for the implementation of the project | | | PC-10ability to use information resources: modern information technologies and graphic editors for the implementation and creation of documentation on design projects | | | | organizational and managerial activities:PC-11 | | willingness to lead a team in the field of their professional activities and make management decisions based on regulatory legal acts; | | | | research activities:PC-12 | | the ability to apply scientific research methods when creating design projects and justify the novelty of their own conceptual solutions | | | | pedagogical activity: |
| PC-13the ability to plan the educational process, perform methodological work and independently conduct lectures and practical classes in general education organizations, vocational education organizations, additional education organizations | | …» [10]. Table 4 "…List of competencies of the FGOS generation 3++ (direction 54.03.01 "Design", profile "Graphic Design") taking into account the requirements of employers (2017, project)code | Generalized labor functions | Labor functions | code | | name | qualification level | name | code | qualification level (sublevel) | PC-1/OTF V-TF V/01.6 | | | In | Design of objects of visual information, identification and communication |
6 | Preparation and coordination with the customer of a project assignment for the creation of objects of visual information, identification and communication | In/01.6 | 6.1 | | PC-1.1 | | Is able to discuss with the customer issues related to the preparation of a project assignment for the creation of an object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-1.2 | Capable of pre-processing sketches of the object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-1.3 | Is able to plan and coordinate with the management of the stages and deadlines for the design project of the object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-1.4 | Is able to make a project assignment for the creation of an object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-1.5 | Able to coordinate with the customer and approve the project assignment for the creation of an object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-2/OTF V-TF V/02.6 | In |
Design of objects of visual information, identification and communication | 6 | Artistic and technical development of design projects of objects of visual information, identification and communication | In/02.6 | 6.2 | | PC-2.1 | | Is able to study the information necessary to work on the design project of the object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-2.2 | Able to determine the compositional techniques and stylistic features of the projected object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-2.3 | Able to develop a design layout of an object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-2.4 | Able to coordinate the design layout with the customer and management | | PC-2.5 | Able to prepare graphic materials for transfer to production | | PC-3/OTF V-TF V/03.6 |
In | Design of objects of visual information, identification and communication | 6 | Author's supervision over the execution of works on the production of visual information, identification and communication objects in production | In/03.6 | 6.3 | | PC-3.1 | | Is able to select the indicators necessary to verify the quality of manufacturing in the production of the projected object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-3.2 | Is able to choose means of quality control of reproduction of the projected object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-3.3 | Is able to carry out quality checks of the manufacturing of the projected object of visual information, identification and communication according to selected indicators | | PC-3.4 | Is able to prepare a conclusion on the results of quality control of the manufacturing of the projected object of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-4/OTF S-TF S/01.7 | With | Development of visual information, identification and communication systems |
7 | Conducting pre-project design research | C/01.7 | 7.1 | | PC-4.1 | | Able to track trends and trends in the design of objects and visual information systems, identification and communication | | PC-4.2 | It is capable of monitoring existing analogues of projected objects and visual information, identification and communication systems | | PC-4.3 | Able to study the needs and preferences of the target audience of the projected objects and systems of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-4.4 | Able to track changes in the legislative and regulatory framework related to the design of objects and systems of visual information, identification and communication | | PC-4.5 | He is able to formalize the results of design research and form proposals for areas of work in the field of design of objects and systems of visual information, identification and communication | …» [11, 12] Note that quoted in Table.2 professional standard the standard was prepared by order of the developer organization "Russian Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs" (OOR, Moscow). The authors are two colleges, six educational institutions of higher education and the Expert Council on Business Technologies in the field of publishing and Printing.
The educational model of specialized design education inherits the best "developments" of Soviet vocational education.Let's explain: a new approach is born at the junction of the solved old problems of Soviet design education, the formation of a creative Person, the value of an intersectoral approach to filling the creative competencies of a designer increases. The Industrial Revolution is becoming part of a real digital society. The challenges it brought first came to the IT industry at the end of the 20th century. There are several scenarios for the development of Russia as a power in the XXI century: restructuring into a new version of the industrial phase with the reanimation of the Soviet legacy, or building a digital economy of services, continuing to sell oil and play on the global raw materials market. In both of these cases, we get a catch-up development of an infinitely developing country in relation to the rest of the world. And there is a less massive, but more promising branch of development. In conditions of self-sufficient conditions (a huge undeveloped territory, a sufficient number of replenished biological resources and the population using them), a developed country with an economy and society built on new technologies, local production and mass inclusion of people in difficult work. This requires a new type of education, where the key figure is choosing the right priorities for applicants of generation Z and younger. Based on the analysis of studies by Vodiakh S.A. [3], Gnatyshina E.A., Gerdt N.A. [4], Senashenko V.S. [13], Henner E. K. [14], the author of the article concluded that the "mixed" educational model of the HSE School of Design carries a clear emphasis on the solution purely practical tasks of the digital society. When forming the educational model of the HSE School of Design, the approach is taken as a basis that "... competence is primarily a behavioral characteristic that is causally related to the criteria for effective and/or successful action in professional or life situations." [14]. Synthesis is more important than analysis, students demand the desire to learn and master new technologies, therefore, in the process of studying, students of all areas of the HSE School of Design master basic knowledge, skills and abilities in various areas of design in teamwork on projects. The author of the article agrees that when forming a design bachelor's degree, regardless of whether applied or academic, the competence of a person as a professional should be put at the forefront. Aspects of the practice-oriented approach of the School of Design are close to the activity approach in education, i.e. the formation of students' personality in professional activity. This is relevant for designers of generation Z (millennials) in their further development in the professional field. For them, the goals of learning to learn quickly are important, which means acquiring good learning skills. First of all, this is the ability to retrain, critically refers to past experience, retrain, mastering the current knowledge base and applying it here and now. To acquire not so much subject knowledge as cognitive skills - to think and solve complex problems. These aspects relate to overprofessional skills, the so-called soft skills. The map of creative competencies is, in fact, the quintessence of creative tasks for creating a project in the professional field. Thus, creative competence as a category of "Maps of creative competencies" is interpreted by the authors from the School of Design as professional competence. On the question of the demand for practice-oriented education. Modern educational programs are formed taking into account the opinion of customers (professional standards). However, not only young people become students, but also, taking into account the aging of the world's population, a large niche of education will be occupied by short- and long-term educational programs aimed at the older generation, which was formed from the point of view of the "knowledge" learning paradigm [14]. They are more characterized by an assessment of the world from the point of view of the traditional educational paradigm of ZUN (knowledge-skills-skills). The most complete and detailed analysis of the interaction and aspect of the relationship of the "knowledge" learning paradigm through the categories of concepts "learning outcomes", "knowledge", "skills" and "competencies" is also discussed in the European educational community in connection with the development of the so-called "European Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning" (European Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning http://www.ehea.info/index.php . In studies in all countries and different systems of Europe, the Unified Qualification Framework is divided into 8 levels reflecting different levels of education. The Unified Framework of Qualifications of the ERC was developed by the European Commission (2004-2008), it has 8 levels that cover the entire education system and determine the scale of qualifications – from the basic level (high school graduation certificate) to advanced (doctorate degree).
Each of the eight levels is defined by a set of descriptors that describe learning outcomes relevant to all qualifications of a given level in any qualification system. Levels are defined and agreed in terms of learning outcomes and described through Knowledge, Skills and Competencies [15]. At this stage of reforms in the Russian design bachelor's and master's degree programs, it is necessary to carefully build interaction with the Western system of qualification categories and "Do not throw the child out with water when bathing" (as in the Russian proverb). The map (matrix) of creative (creative) competencies (analogous to the competence matrix) is formed by leading profile experts (design and advertising professionals).Let's explain this evaluation criterion in a bit of history. The design at HSE began in 2013-2014. By joining (with an autonomous form of interaction) HSE has restructured the MIEM Technical University (Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics). Previously, the Department of "Engineering and Machine Graphics" of MIEM (Head of the Department Alexander Vladimirovich Verkhovsky) in 1999, in the wake of a request for design personnel at a technical university, organized training in the creative specialty "Design" (specialties "Graphic Design", "Web Design", "Cinema, photo and video design). With the reorganization of MIEM by joining the HSE, the guidelines have also changed. The Department of IiMG became the Department of Design of the MIEM of the Higher School of Economics (head, PhD, Associate Professor Ulyana Viktorovna Aristova), then 2 areas of training "Graphic Design", "Web Design") they became the basis of the Faculty of Design, and at the moment the HSE School of Design. The organization of the design direction at the HSE School of Design began in 2013 and continues to be engaged in Rivchun Tatiana Evgenievna (advisor to the Rector Ya.I. Kuzminova, Deputy Dean of the Faculty of Communications, Media and Design A.G. Bystritsky) and Meshcheryakov Arseniy Vladimirovich (head of the School of Design). A team of professionals from specialized advertising and design bureaus, branding and creative agencies "Agey-Tomesh", "Books of WAM", "Artonika", Arbeitskollektiv, Ostengruppe, etc. in 2014 laid the foundations of the strategy of the HSE School of Design, which anticipated the trend of restructuring educational standards (FGOS 3++) [9, 10, 11, 12] from the point of view of introducing professional standards of the digital society. The main methodological technique is the practice-orientation of the main educational program (OOP / OPOP). At the head of each profile area of training is one or a team of experts (art directors, owners of design bureaus, leading designers, artists, etc.). They form the content of the curriculum in terms of the demand for the skills being formed, performance competence, trends (Eng. a clear, pronounced trend) in the design field, demand graduates in the labor market. The requirements for the recruitment of personnel to ensure the educational process are high for teachers. The author of the article, while working at the HSE (from January 2013 to August 2014), made a feasible contribution to the collection of data for the formation of a map of creative competencies. A number of in-depth interviews with employers (authors of teaching methods at the HSE School of Design) were conducted in terms of the structure and completeness of filling the level of competence development with didactic units. The author thanks the management of the Faculty of Design of the Higher School of Economics (renamed the HSE School of Design in 2014) for the opportunity to work with curators and students in terms of collecting and processing information during this research. This study formed the basis of the research conducted by the author in the field of development of creative activity (creativity) of students of higher education institutions:. The student portfolio is available for free access for review 24/7.The student portfolio of the HSE School of Design is a user-friendly (ergonomic) resource, informative and replenished daily. The thematically structured archive of projects introduces potential employers to projects, authors and shows the level of professionalism and education of students [8]. The current and ultimately cumulative (cumulative) student rating is mainly formed from the evaluation of project-oriented disciplines of the curriculum (Table 1). The practice-oriented educational model is realized by communicating directly with curators and customers within the framework of the project.In the course of training, junior students from designing abstract, invented the most fantastic projects move on to communicating with real customers in real order mode in the 3rd and 4th courses. Customers are business people, and they are not always loyal to students' deadlines due to bad weather or lack of inspiration. Good training when communicating with customers is guaranteed, because in the work comes an understanding of interpersonal interaction within the framework of solving aspects of professional competencies. Conclusion.Thus, within the framework of this study, the author analyzes the solution of a practice-oriented task (using the example of the HSE School of Design) in conditions of effective management
A modern approach to training designers for a digital society through the formation of creative competencies in terms of aspects of solving practice-oriented tasks of changing generations of applicants is possible with the provision of the following conditions (evaluation criteria): 1. A wide range of creative profiles within the framework of the "Design" training area.2. The map (matrix) of creative (creative) competencies is formed by leading profile experts (design and advertising professionals). 3. The educational model of specialized design education inherits the best "developments" of Soviet vocational education; 4. The student portfolio is available for free access for review 24/7. 5. The practice-oriented educational model is implemented by communicating directly with curators and customers within the framework of the project.
References
1. Atlas novykh professii. ‒ 2021. ‒ http://atlas100.ru ‒ (Data obrashcheniya 29.07.21)
2. Entsiklopediya professional'nogo obrazovaniya: V 3-kh t. / Pod red. S. Ya. Batysheva. M.: APO, 1998.‒ 568 s., il.
3. Vodyakha S.A. Kreativnaya kompetentnost': podkhody k izmereniyu [Tekst] / S.A. Vodyakha // Otsenka kachestva obucheniya v obrazovatel'nykh uchrezhdeniyakh: sb. nauch. st. Vseros. nauch.-prakt. konf. — Ekaterinburg: Ural'skii gosudarstvennyi pedagogicheskii universitet. — 2012. — S. 28–33.
4. Gnatyshina E.A., Gerdt N.A. Model' formirovaniya professional'no-tvorcheskogo potentsiala studentov tvorcheskikh professii. // Obrazovanie i nauka. ‒ 2015. ‒ ¹ 1(2) ‒ S. 18-27. ‒ DOI: 10.17853/1994-5639-2015-2-18-27
5. Karta kreativnykh kompetentsii Shkoly dizaina NIU VShE. ‒ 2021. ‒ https://creativemap.hse.ru/timetable/1244. ‒ (Data obrashcheniya 29.07.21).
6. Coursera-obrazovatel'naya platforma. ‒ 2021. ‒ https://www.coursera.org. ‒ (Data obrashcheniya 29.07.21).
7. Itten I. Iskusstvo formy. ‒ M.: Izd.D.Aronov, 2001. ‒ 136 s.
8. Studencheskoe portfolio Shkoly dizaina NIU VShE. ‒ 2021. ‒ https://portfolio.hse.ru. ‒ (Data obrashcheniya 29.07.21)
9. Strategiya nauchno-tekhnologicheskogo razvitiya Rossiiskoi Federatsii na dolgosrochnyi period. ‒ 2021. ‒ http://sntr-rf.ru/materials/strategiya-nauchno-tekhnologicheskogo-razvitiya-rossiyskoy-federatsii-na-dolgosrochnyy-period/#comment ‒(Data obrashcheniya 29.07.21).
10. FGOS VO Prikaz Minobrnauki Rossii ot 11 avgusta 2016 g. ¹ 1004 «Ob utverzhdenii federal'nogo gosudarstvennogo standarta vysshego obrazovaniya po napravleniyu podgotovki 54.03.01 Dizain (uroven' bakalavriata) (Zaregistrirovan v Minyuste Rossii 25.08.2016 g. ¹ 43405)
11. Prikaz Ministerstva truda i sotsial'noi zashchity RF (Mintrud Rossii) ot 17 yanvarya 2017 g. ¹ 40n «Ob utverzhdenii professional'nogo standarta «Graficheskii dizainer»» (zaregistrirovan Ministerstvom yustitsii Rossiiskoi Federatsii 27 yanvarya 2017 g., registratsionnyi ¹ 45442) .
12. FGOS VO Prikaz Minobrnauki Rossii ot 13 avgusta 2020 g. ¹ 1015 «Federal'nyi gosudarstvennyi obrazovatel'nyi standart vysshego obrazovaniya – bakalavriat po napravleniyu podgotovki 54.03.01 Dizain. (Zaregistrirovan v Minyuste Rossii 27.08.2020 ¹ 59498).
13. Senashenko V.S. (2018) Urovni sopryazheniya sistemy vysshego obrazovaniya i sfery truda // Vysshee obrazovanie v Rossii.‒ 2018. ‒ T. 27. ¹ 3. ‒ S. 38-47. ‒ DOI: 10.31992/0869-3617-2019-28-4-9-20
14. Khenner E. K. Professional'nye znaniya i professional'nye kompetentsii v vysshem obrazovanii // Obrazovanie i nauka. ‒ 2018. ‒ T. 20. ‒ ¹ 2.‒ S. 9–31. DOI: 10.17853/1994-5639-2018-2-9-31
15. Demchuk A., Karavaeva Y., Kovtun Y., Rodionova S. Competencies, learning outcomes and forms of assessment: The use of Tuning Methodology in Russia. Tuning Journal for Higher Education. ‒ 2015. ‒ V. 3. ¹ 1.‒ P. 149-185. ‒ http://www.tuningjournal.org/article/view/97/1089. ‒ (Data obrashcheniya 29.07.21)
| 















 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.

 Eng
Eng


